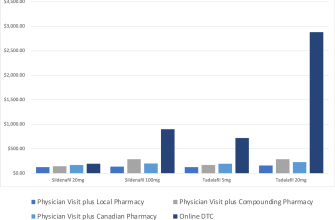
Fluconazole stands out as a widely used antifungal medication, primarily combating infections caused by fungi such as Candida. This medication effectively treats various conditions, including vaginal yeast infections, oral thrush, and systemic fungal infections. When seeking effective treatment options, fluconazole often comes highly recommended due to its convenient dosing and proven efficacy.
When prescribed fluconazole, patients typically follow a regimen that relies on their specific infection type and severity. For instance, a single dose may suffice for uncomplicated vaginal infections, while a more extended course is necessary for severe or systemic cases. Adhering closely to the treatment plan is crucial for a successful outcome.
Potential side effects, such as headaches, gastrointestinal discomfort, or allergic reactions, may occur, though many individuals tolerate fluconazole well. Monitoring for these effects ensures any concerns are addressed promptly, allowing for swift adjustments to the treatment if necessary.
In summary, fluconazole serves as an effective tool in the fight against fungal infections, offering a reliable option for those seeking relief. Consultation with a healthcare provider ensures the appropriate use and management of this medication, aligning treatment closely with individual health needs.
- Comprehensive Guide to Fluconazole
- Usage Recommendations
- Side Effects and Precautions
- What is Fluconazole and How Does it Work?
- Common Indications for Fluconazole Use
- Candidemia
- Cryptococcal Meningitis
- Dosage Guidelines for Adults and Children
- Possible Side Effects of Fluconazole
- Drug Interactions and Contraindications
- Key Drug Interactions
- Contraindications
- Additional Considerations for Special Populations
- How to Store and Handle Fluconazole Safely
- Storage Tips
- Handling Instructions
Comprehensive Guide to Fluconazole
Fluconazole is a powerful antifungal medication primarily used to treat infections caused by fungi and yeast. It targets specific conditions, including candidiasis, cryptococcal meningitis, and fungal infections in individuals with compromised immune systems. For effective treatment, follow prescribed dosages, typically taken once daily, and maintain consistent timing to enhance absorption.
Usage Recommendations
When using fluconazole, it is critical to communicate any medical history with your healthcare provider, particularly concerning liver disease or drug allergies. Monitor for potential interactions with other medications, such as warfarin or certain anticonvulsants. Pregnant women should only take fluconazole when deemed necessary, as potential risks to the fetus exist.
Side Effects and Precautions
Common side effects include headaches, dizziness, and gastrointestinal issues like nausea or diarrhea. Severe allergic reactions are rare but require immediate medical attention. Regular liver function tests are advisable for prolonged use. Always keep your healthcare provider informed about any adverse effects experienced during treatment.
What is Fluconazole and How Does it Work?
Fluconazole is an antifungal medication primarily used to treat infections caused by fungi and yeast, including Candida species. It effectively combats various fungal infections, making it a popular choice among healthcare providers.
This medication works by inhibiting the synthesis of ergosterol, a critical component of the fungal cell membrane. By disrupting this process, fluconazole weakens the structure of the cell membrane, leading to cell death and preventing the growth of fungi.
Fluconazole is often prescribed for conditions such as oropharyngeal candidiasis, esophageal candidiasis, and systemic fungal infections, including cryptococcal meningitis. It can be administered orally or intravenously, depending on the severity of the infection and the patient’s condition.
The usual dosage varies based on the type and location of the infection. For oral thrush, the typical recommendation is a single 200 mg dose, followed by 100 mg daily for at least two weeks. Always follow the healthcare provider’s instructions for the most effective treatment outcome.
While fluconazole is generally well-tolerated, some side effects may occur, including nausea, headache, and abdominal pain. Serious allergic reactions, although rare, necessitate immediate medical attention.
As with any medication, interactions with other drugs are possible. Patients should inform their healthcare provider of all medications they are taking to avoid any adverse effects.
| Indication | Administration | Typical Dosage |
|---|---|---|
| Oropharyngeal Candidiasis | Oral | 200 mg first day, then 100 mg daily |
| Esophageal Candidiasis | Oral/IV | 200 mg first day, then 100-200 mg daily |
| Cryptococcal Meningitis | IV | Initial 400 mg, then 200 mg daily |
Always consult your healthcare provider for tailored advice and treatment plans. Fluconazole serves as a reliable option for managing fungal infections when used appropriately.
Common Indications for Fluconazole Use
Fluconazole is primarily prescribed for the treatment of various fungal infections. It effectively combats conditions like candidiasis, which can manifest in different areas such as the mouth (oral thrush), throat, and vagina. Healthcare providers recommend fluconazole to address these infections efficiently, particularly in patients without severe comorbidities.
Candidemia
Fluconazole serves as a treatment option for candidemia, a bloodstream infection caused by fungi. This medication works effectively in immunocompromised patients or those undergoing intensive care. Monitoring patient response is crucial, as adjustments to dosage may be necessary based on clinical outcomes.
Cryptococcal Meningitis
Another significant indication for fluconazole is cryptococcal meningitis, especially among individuals with HIV/AIDS. The treatment regimen often begins with a high dose, followed by maintenance therapy to prevent recurrence. Regular follow-ups ensure adequate monitoring of the infection and any potential side effects from the medication.
In addition to these common uses, fluconazole also proves beneficial in treating fungal infections related to other conditions, such as preventative treatment after bone marrow transplants. Always consult with a healthcare professional for tailored treatment plans and appropriate dosages.
Dosage Guidelines for Adults and Children
The standard dosage of fluconazole for adults is typically 150 mg as a single dose for treating vaginal candidiasis. For other types of infections, such as oropharyngeal candidiasis, the initial dose may range from 200 mg to 400 mg, depending on the severity of the condition. Daily doses can vary, but common regimens include 100 mg to 400 mg daily for up to 14 days.
In adults with cryptococcal meningitis, the recommended initial dosage is 400 mg on the first day, followed by 200 mg to 400 mg once daily. This treatment usually lasts for several weeks, often extending to a minimum of 10 weeks.
For children, fluconazole is dosed based on weight. For those aged 6 months to 12 years, the guideline suggests an initial dose of 6-12 mg/kg, with a maximum dose of 400 mg. After the initial administration, a maintenance dose of 3-6 mg/kg daily can be applied, tailoring it to the infection type. Keep in mind that children under 6 months should have a dosage of 3 mg/kg as a starting point.
Continue to monitor both adults and children for responses to the medication, adjusting dosages if necessary based on the clinical situation and any side effects that may arise.
Possible Side Effects of Fluconazole
Fluconazole can lead to various side effects. Commonly reported effects include headaches, dizziness, and gastrointestinal disturbances like nausea and abdominal pain. Monitor your body’s reaction, as these symptoms may indicate an intolerance to the medication.
More serious side effects, though rare, can also occur. Be alert for signs of liver problems, such as jaundice, dark urine, or persistent fatigue. If you notice any of these symptoms, seek medical advice immediately.
Allergic reactions, such as rash, itching, or swelling, can happen. If you experience any of these symptoms, discontinue use and consult your healthcare provider.
Some individuals may experience skin reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, a severe condition requiring urgent medical attention. Any unusual skin changes should prompt a discussion with your doctor.
Fluconazole can interact with several other medications, leading to an increased risk of side effects. Always inform your healthcare provider of all the medications you are taking to avoid potential interactions.
Regular monitoring through blood tests may be necessary to track liver function and drug levels, particularly for long-term use. Communicate with your healthcare team about any concerns or emerging symptoms during treatment.
Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice tailored to your individual health needs when considering fluconazole.
Drug Interactions and Contraindications
Fluconazole interacts with several medications, necessitating caution. It is crucial to avoid combining fluconazole with drugs that are metabolized by CYP2C19, as fluconazole can increase their levels and potential side effects. Medications like clopidogrel may require careful monitoring when taken alongside fluconazole.
Key Drug Interactions
When considering fluconazole, be aware of its interaction with other antifungals such as voriconazole and itraconazole, as concurrent use can lead to increased plasma concentrations. Combining fluconazole with benzodiazepines, particularly triazolam, could result in heightened sedation effects.
Additionally, fluconazole may enhance the effects of medications like warfarin, increasing bleeding risks. Regular INR monitoring is advisable for patients on anticoagulants.
Contraindications
Fluconazole is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to the drug or other azole antifungals. Use during pregnancy requires careful consideration due to potential risks to the fetus, especially in the first trimester. Always discuss your medication regimen with a healthcare provider to ensure safe use of fluconazole.
Knowing these interactions and contraindications helps in optimizing treatment while minimizing risks to your health. Always consult a healthcare professional before making any changes to your medication plan.
Additional Considerations for Special Populations
Pregnant individuals should use fluconazole cautiously. Studies indicate potential risks to the fetus, particularly in the first trimester. Consultation with a healthcare provider is necessary to evaluate the risks and benefits in each case.
Pediatric patients may require dose adjustments based on weight and age. Monitoring for efficacy and adverse effects is crucial, as younger populations might metabolize the drug differently than adults.
Individuals with renal impairment should receive careful monitoring. Dosage modifications are often necessary, as fluconazole is primarily eliminated through the kidneys. Regular renal function tests can help guide therapy.
Elderly patients may have altered pharmacokinetics due to age-related changes in drug metabolism and clearance. Assessing their overall health status, including liver and kidney function, ensures safe administration.
Those with liver disease face increased risks of toxicity. Regular liver function tests come highly recommended to adjust doses and prevent adverse effects.
Patients taking other medications may experience drug interactions. Always evaluate current medications to avoid harmful effects. A robust medication review can enhance safety.
Individuals with immunocompromised states should receive more vigilant monitoring. Increased susceptibility to infections warrants a stronger approach to infection management while on fluconazole.
How to Store and Handle Fluconazole Safely
Store fluconazole at room temperature, away from excess moisture and heat. Keep it in a tightly closed container, and ensure it is out of reach of children and pets.
Storage Tips
- Avoid storing fluconazole in the bathroom, as humidity can affect its quality.
- Check the expiration date regularly and dispose of expired medication properly.
- Do not refrigerate or freeze fluconazole unless specifically instructed by a healthcare professional.
Handling Instructions
- Wash your hands before handling the medication.
- Use the prescribed dosage measuring tool for accuracy.
- If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it’s close to the next dose, skip the missed one, and continue your schedule.
- Return unused or expired fluconazole to a pharmacy or follow local disposal guidelines to prevent environmental contamination.
By following these guidelines, you ensure that fluconazole remains effective and safe for your use.